Half body CPR training manikin(Sim....

BIX/CPR100A
Advanced fully automatic electroni....
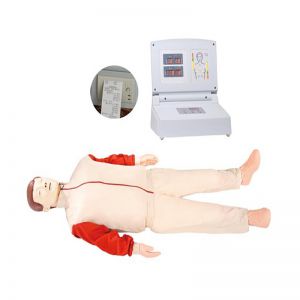
BIX/CPR480
Advanced computer half body CPR ma....

BIX/CPR260
Advanced infant head for trachea i....
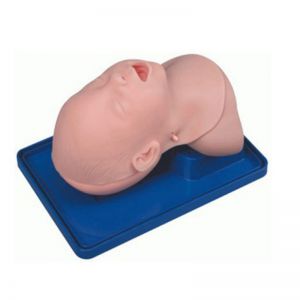
BIX-J3A
Neonate Head for trachea Intubatio....

BIX-J2A
Created on:2024-11-22 | bomn
Article tag: Anatomical models of the kidney Organ anatomical model
In the vast field of medical education, renal anatomical model is undoubtedly a bridge connecting theory and practice, abstraction and i...
In the vast field of medical education, renal anatomical model is undoubtedly a bridge connecting theory and practice, abstraction and intuition. With its unique shape and fine structure, it provides an excellent platform for medical students, doctors and researchers to intuitively understand the structure of the kidney.
Kidney, as an important excretory organ of human body, has a complex and fine structure, including kidney parenchyma and renal pelvis. The renal parenchyma is further subdivided into cortex and medulla, in which the cortex is rich in glomeruli and renal tubules, and is the main place for filtration and reabsorption of the kidney. The medulla, on the other hand, contains several renal cones with a collecting duct system that directs urine to the renal pelvis.

Through highly simulated design, these complex structures of the kidney are presented one by one. The model not only shows the external morphology of the kidney, such as smooth envelope and protruding renal papillae, but also reveals its internal structure, such as the boundary between cortex and medulla, the distribution of glomeruli, the direction of renal tubules and the arrangement of collecting tubes. This intuitive and three-dimensional display enables learners to quickly grasp the key features of the kidney structure and deepen their understanding of the physiological function of the kidney.
In addition, it is highly interactive and maneuverable. Learners can interact deeply with the model through touch, observation, disassembly, etc., so as to understand every detail of the kidney more deeply. This way of learning not only improves learners' interest and enthusiasm in learning, but also promotes their in-depth thinking and exploration of kidney structure.
In medical education, the application value is self-evident. It not only helps students quickly grasp the basics of kidney structure, but also provides strong support for their clinical practice. Through the model's assisted learning, students can more accurately identify the signs and symptoms of kidney disease, and provide a scientific basis for the development of effective treatment programs.
In short, renal anatomical model has become an indispensable part of medical education with its intuitive, three-dimensional and interactive characteristics. It not only helps students gain a deeper understanding of the kidney structure, but also provides strong support for their clinical practice.