Half body CPR training manikin(Sim....

BIX/CPR100A
Advanced fully automatic electroni....
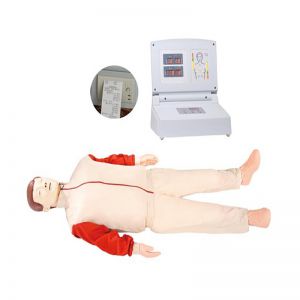
BIX/CPR480
Advanced computer half body CPR ma....

BIX/CPR260
Advanced infant head for trachea i....
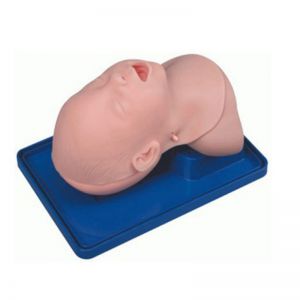
BIX-J3A
Neonate Head for trachea Intubatio....

BIX-J2A
Created on:2024-12-30 | bomn
Article tag: Upper limb skeletal model A human skeleton model BIX-A1031
The upper limb bone model is undoubtedly an important tool in medical education to enhance clinical diagnostic ability. Through its intuitive and interactive features, medical students can not only deepen their understanding of anatomical structures, but al...
As an important auxiliary tool in medical education, upper limb bone model is widely used in anatomy teaching, surgical training and clinical diagnosis. For medical students, being able to intuitively and repeatedly learn the structure, function and clinical application of bone through physical models is helpful to improve their clinical diagnostic ability. This paper will discuss the role, academic support and clinical significance of upper limb skeletal model in improving clinical diagnostic ability.
Relationship between upper limb skeletal model and clinical diagnostic ability
1. Enhance anatomical understanding and clinical thinking
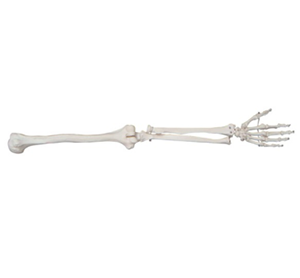
The upper limb bone model provides medical students with a three-dimensional, tactile, realistic learning tool to help them gain a deeper understanding of the structure and function of the upper limb bones. By observing the model, students can not only understand the relative positions of various bone parts, but also touch key anatomical structures such as joints and muscle attachment points. This intuitive experience is more teaching than simple maps or two-dimensional drawings.
According to research, medical students can improve the accuracy of anatomy knowledge by about 30% compared with traditional teaching methods through practical training of upper limb bone model. This combination of theory and practice greatly enhances students' clinical thinking ability and spatial imagination, thus laying a solid foundation for subsequent clinical diagnosis.
2. Simulate clinical diagnosis and operation
Through the upper limb bone model, students can perform simulated diagnoses to identify fractures, joint dislocations, and other common sports injuries. For example, by simulating the structural changes in the upper limb after a fracture, students can learn how to identify the location and type of injury through palpation, imaging, and other methods combined with the model. Simulation training can also help students better grasp how to use clinical knowledge to make diagnoses, thereby improving the accuracy of actual diagnosis and treatment.
3. Improve diagnostic speed and accuracy
A study of medical simulation education showed that students using upper limb bone models were 20 percent faster and 25 percent more accurate in fracture diagnosis and treatment options than students who did not use models. This improvement comes not only from the operability of the model itself, but also from the students' enhanced hand-eye coordination and three-dimensional cognition of anatomy during the learning process.
4. Enhance multi-angle clinical problem solving ability
The upper limb bone model also helps students analyze clinical problems from multiple perspectives. For example, the model can be used to simulate the movement patterns of bones and joints under different postures and movement modes, as well as the mechanism of sports injury. This multi-angle and dynamic way of learning enables students not only to understand a single pathological phenomenon, but also to master complex clinical problems and improve the overall diagnostic ability.
Academic support and data
A number of academic studies have shown that simulation models have a significant effect on improving clinical diagnostic ability. An experimental study conducted in the United States showed that medical students who learned anatomy using a model of the bones of the upper limb improved the accuracy of diagnosis of bone injuries and related diseases by 28% compared with traditional teaching methods. In addition, the model has been widely recognized for helping students develop correct anatomical thinking and surgical skills.
Clinical significance
In clinical practice, accurate diagnosis is the key to ensure the effectiveness of treatment. By providing a realistic, actionable learning platform, the upper limb bone model enables students to practice repeatedly in a simulated environment, thereby enhancing their confidence and competence in clinical diagnosis. More importantly, this model allows students to perform multiple practices without directly touching patients, reducing clinical errors and improving the safety of diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
The upper limb bone model is undoubtedly an important tool in medical education to enhance clinical diagnostic ability. Through its intuitive and interactive features, medical students can not only deepen their understanding of anatomical structures, but also improve diagnostic accuracy and the ability to deal with complex conditions in simulated diagnosis and treatment processes. With the continuous development of medical education, upper limb skeletal model will play an increasingly important role in medical training in the future.