Half body CPR training manikin(Sim....

BIX/CPR100A
Advanced fully automatic electroni....
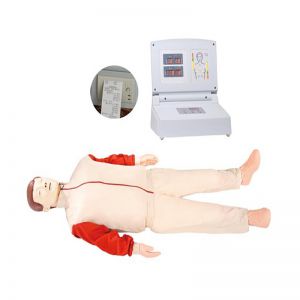
BIX/CPR480
Advanced computer half body CPR ma....

BIX/CPR260
Advanced infant head for trachea i....
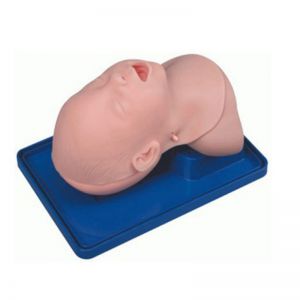
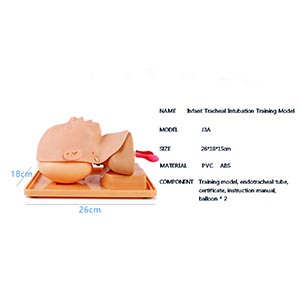
BIX-J3A
Neonate Head for trachea Intubatio....

BIX-J2A
Created on:2025-01-13 | bomn
The Advanced Infant Tracheal Intubation model helps healthcare professionals master airway management skills by providing a safe, realistic training environment. It can not only improve the accuracy of individual intubation operations, but also enhance team...
For medical professionals, especially in the field of pediatrics, tracheal intubation is an important skill for rescuing infant patients. The Advanced Infant Tracheal Intubation model provides participants with a highly simulated, actionable training platform to effectively improve clinical airway management skills. Here are a few ways in which personal growth and skill development can be facilitated through this teaching model:
1. Provide a safe practice environment
Infant airways, unlike those of adults, are small and fragile, which makes tracheal intubation techniques very demanding. The Advanced Infant Tracheal Intubation model provides a simulated training environment that allows participants to practice intubation skills repeatedly without risk. This repeated practice helps students familiarize themselves with the anatomy of the airway and the problems that may be encountered during intubation, reducing practical clinical errors.
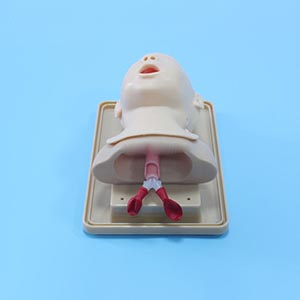
Infant Tracheal intubation model
2. Precise physiological feedback
Modern advanced infant tracheal intubation models have precise physiological feedback functions. When students perform endotracheal intubation, the model can simulate the actual response of the airway, such as chest rise and fall, airway resistance changes, etc. With this immediate feedback, students can sense if they are doing something correctly and adjust their technique in time to improve the accuracy of their skills.
3. Simulate complex airway problems
The advanced model can not only simulate the normal intubation process, but also simulate various complex airway conditions, such as airway obstruction and laryngeal edema. This enables students to conduct emergency training in different situations and improve their ability to respond to complex clinical situations. The variety of simulations ensures that participants are more comfortable in the face of real cases.
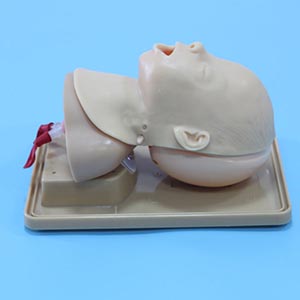
4. Improve teamwork and communication skills
Clinical airway management is often a team effort. In the training of the advanced infant Tracheal intubation model, students can perform intubation operations in a collaborative team environment and improve communication and coordination with other team members. By simulating the actions of different roles, participants are able to better understand the impact of each step on airway management.
5. Data-supported learning effect tracking
The advanced Infant Tracheal intubation model records detailed data about each operation, including intubation time, success rate, and procedure accuracy. These data provide participants with objective assessment criteria and a clear picture of their potential for improvement. Data support also allows teachers to guide students according to their weaknesses to ensure maximum learning results.
Data support:
One study showed that participants trained with an advanced infant tracheal intubation model improved intubation success rates by about 30% over traditional training methods. In addition, participants who underwent simulated training in the actual clinical intubation operation time was reduced by an average of 20%, and the success rate was increased by 15%.
The Advanced Infant Tracheal Intubation model helps healthcare professionals master airway management skills by providing a safe, realistic training environment. It can not only improve the accuracy of individual intubation operations, but also enhance team collaboration and enhance learning through data support. For medical students and professional physicians, this model is undoubtedly an effective tool to improve clinical airway management skills.