Half body CPR training manikin(Sim....

BIX/CPR100A
Advanced fully automatic electroni....
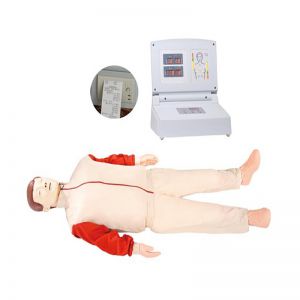
BIX/CPR480
Advanced computer half body CPR ma....

BIX/CPR260
Advanced infant head for trachea i....
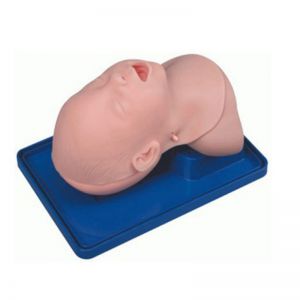
BIX-J3A
Neonate Head for trachea Intubatio....

BIX-J2A
Created on:2025-02-26 | bomn
The application of thoracic puncture and drainage training model in medical education, especially in improving clinical skills, plays an important role. Simulation training can effectively improve students' operational skills to help them reduce errors ...
Thoracic puncture and drainage training model is a very important training tool in medical education, especially for medical students. As a common first aid and treatment operation, thoracic puncture drainage has important clinical significance for many clinical diseases, such as pneumothorax and pleural effusion. However, due to the high technical requirements for doctors, and there are certain risks in the operation process, the role of simulation training is more prominent. Through effective training models, not only can improve clinical skills, but also enhance students' emergency response ability, thus improving the overall medical level.
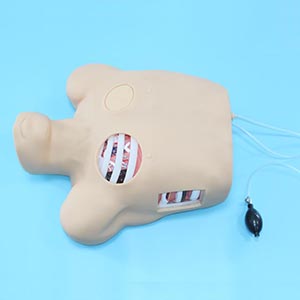
Thoracic puncture Drainage training model
Clinical significance
Thoracic puncture drainage is a common method in clinical treatment of pleural effusion, pneumothorax and other diseases. In these cases, timely and accurate drainage can help patients relieve symptoms, improve respiratory function, and even save lives in some cases. However, this technology requires a high level of skill for the operating doctor, because if it is not performed properly, it may cause complications such as pneumothorax, bleeding, infection and so on. Therefore, in clinical practice, through the training of simulation models, medical students can learn how to accurately determine the puncture point, select the appropriate puncture method and master the correct drainage technology in a risk-free environment.
In addition, thoracic puncture drainage often needs to be implemented quickly in emergency situations, and medical personnel must be able to remain calm and make the right decision in a high-pressure environment. Therefore, simulation training not only helps to improve operational skills, but also helps students improve their decision-making ability and reaction speed under pressure.
Data support
A number of studies and clinical practice have shown that thoracic puncture and drainage training model can effectively improve the clinical skills of medical students. In a study conducted at multiple teaching hospitals, for example, researchers assessed the skill mastery of medical students by simulating thoracic puncture and drainage training. The results showed that in the students who received the simulation training, the accuracy of the operation was improved by 28% and the complication rate was significantly reduced.
Another study involving 100 residents showed that after simulation training, the doctors' accuracy in actual clinical procedures improved from 65% to 90%, while the incidence of errors significantly decreased (e.g., misselection of puncture points, improper control of puncture depth, etc.). These data show that simulation training can significantly promote the mastery of skills, reduce errors, and improve the safety and success rate of surgery.
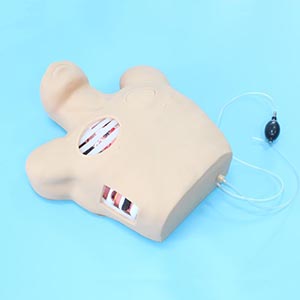
Features of the training model
The training model of thoracic puncture drainage usually includes virtual reality (VR) simulation model, anatomical model and human-machine training equipment. The virtual reality model can provide a highly simulated operating environment, allowing students to experience different clinical situations in the simulation and perform repeated practice. The anatomical model helps students understand the anatomy of the chest, enhancing their spatial awareness and puncture accuracy. The human-machine combined equipment can feedback the operation effect in real time, helping students to correct the error in the operation immediately.
Through these models, students are able to repeatedly practice technical details, become familiar with operational procedures, and learn how to make sound judgments in complex clinical situations without touching real patients.
Clinical skills enhancement
Simulation training can effectively improve students' pleural puncture and drainage skills, especially in the following aspects:
1. Operational accuracy : Through continuous practice, students can improve the accuracy of selecting puncture points and reduce the risk of accidental injury to vital organs.
2. Operational confidence : Simulation training helps to improve students' operational confidence, so that they can make decisions more calmly and quickly in actual operation.
3. Reduce complications : Through simulation training, students can be familiar with common complications and their prevention measures to reduce the risk of operation.
4. Teamwork ability : Thoracic puncture drainage is usually the result of multidisciplinary cooperation, and simulation training can help students improve their communication and collaboration ability with other medical personnel.
Conclusion
The application of thoracic puncture and drainage training model in medical education, especially in improving clinical skills, plays an important role. Simulation training can effectively improve students' operational skills to help them reduce errors and improve patient safety in clinical practice. In addition, the data also show that simulation training has obvious advantages in improving the accuracy of operation, reducing the incidence of complications and improving the self-confidence of doctors. Therefore, it is very important to integrate the training model of thoracic puncture and drainage into the medical education system to train qualified clinicians.