Half body CPR training manikin(Sim....

BIX/CPR100A
Advanced fully automatic electroni....
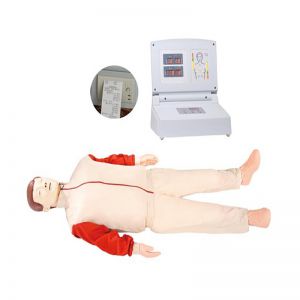
BIX/CPR480
Advanced computer half body CPR ma....

BIX/CPR260
Advanced infant head for trachea i....
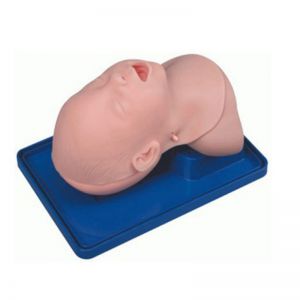
BIX-J3A
Neonate Head for trachea Intubatio....

BIX-J2A
Created on:2025-03-11 | bomn
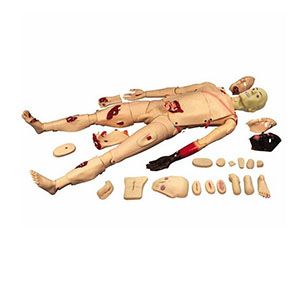
Article tag: Advanced Trauma Model BIX-J110 Trauma Care model
Although traditional trauma training models have some value in basic operational training, they have obvious limitations in meeting the urgent needs of modern trauma medicine. Especially in complex situations such as multiple trauma and traumatic shock, tra...
Traditional trauma training model is widely used in medical education to help medical personnel master the basic skills of trauma treatment. These models are often based on simulators, animal models, or standardized patients and are designed to allow participants to practice initial assessment and handling skills of trauma. However, with the development of modern trauma medicine, especially the high risk and complexity of emergency trauma, whether traditional trauma training models can meet the urgent needs of the current medical environment has gradually become an important topic of concern for industry experts and educators.
Opinions of industry experts
Many industry experts have pointed out that traditional trauma training models, while useful in skills training, are inadequate in meeting the urgent needs of modern trauma medicine. Therefore, the training of modern trauma medicine should gradually shift to a more simulation and dynamic training mode to improve the ability of medical personnel to deal with complex trauma.
1. Scenario simulation and emergency response :
Experts emphasize that modern trauma training should focus on situational simulation, allowing students to operate in a changing clinical environment. This training mode can simulate a variety of emergencies, such as traumatic shock, respiratory failure, organ bleeding, etc., so that students can exercise emergency decision-making and response ability in actual operation. In addition, the situational simulation can simulate sudden complications, such as airway obstruction, cardiac arrest, etc., to help students cope with the complexity of the trauma treatment process.
2. Multidisciplinary team Collaboration Training :
With the increasing importance of teamwork in trauma treatment, experts believe that training models should simulate more teamwork. Through multidisciplinary team training, students can work together with different professionals in emergency situations to complete trauma treatment tasks. This can not only improve the success rate of trauma treatment, but also strengthen the communication and collaboration ability between teams, and improve the overall efficiency of treatment.
Data support and research results
Research shows that high simulation technology can significantly improve the effect of trauma medical training. For example, according to a 2018 study, participants who simulated trauma situations using virtual reality technology had about 30% less time to make decisions during simulated trauma care than participants with traditional models. In addition, the students' operational accuracy has also improved by 20%. Another 2019 study showed that participants in multidisciplinary team training demonstrated 40 percent better teamwork and emergency response skills in simulated trauma care than participants in traditional single-operation training.
In addition, the virtual reality-based trauma simulation system can provide real-time feedback on the trainees' operations and provide dynamic physiological monitoring, such as heart rate, blood oxygen saturation, blood pressure, etc., which enables the trainees to obtain a more realistic experience and timely improvement suggestions when facing complex trauma and sudden complications.
Conclusion
Although traditional trauma training models have some value in basic operational training, they have obvious limitations in meeting the urgent needs of modern trauma medicine. Especially in complex situations such as multiple trauma and traumatic shock, traditional models can not effectively simulate sudden complications and dynamic physiological changes. Therefore, industry experts generally suggest that trauma medicine training should be transformed to high simulation and situational training to improve the emergency response ability and teamwork ability of medical personnel. High simulation technology, multidisciplinary collaborative training and dynamic feedback system will play an increasingly important role in improving the effectiveness of trauma medical training.