Half body CPR training manikin(Sim....

BIX/CPR100A
Advanced fully automatic electroni....
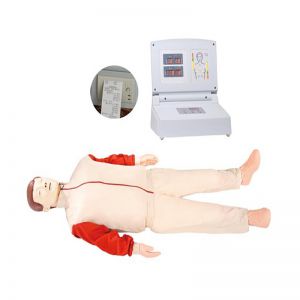
BIX/CPR480
Advanced computer half body CPR ma....

BIX/CPR260
Advanced infant head for trachea i....
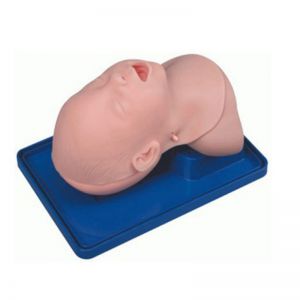
BIX-J3A
Neonate Head for trachea Intubatio....

BIX-J2A
Created on:2024-01-16 | bomn
Article tag: cpr model cpr OPERATION cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a first-aid measure to rescue cardiac arrest patients by artificially maintaining brain function until natural breathing and blood circulation are restored
...Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (cpr) is a first-aid measure to rescue cardiac arrest patients by artificially maintaining brain function until natural breathing and blood circulation are restored
cpr is not a single technique; it encompasses a series of assessments and actions. In addition, the steps of cpr may need to be modified according to different causes of cardiac arrest. George Crile, in 1903, reported the first successful use of external chest compressions in a dog model. The following year, he reported the first case of human closed-chest cardiac massage in the United States. In 1906, he demonstrated how an infusion of saline and epinephrine, combined with chest compressions, could successfully resuscitate a patient in cardiac arrest. Therefore, in 1949, if they encountered someone who needed first aid, they would only perform chest compressions. There was no technology to breathe and provide oxygen at that time. In 1954 James Elam was the first to demonstrate that exhaled air was sufficient to maintain adequate oxygenation. In 1956, Peter Safar and James Elam invented mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (cpr) was developed in 1960. The American Heart Association has launched a program to familiarize physicians with external thoracic cardiopulmonary resuscitation and serve as pioneers in cpr training for the public. In 2008, the American Heart Association issued a statement on Hands-Only™ cpr, stating that bystanders who witness an adult suddenly collapsing should call 911 and provide high-quality chest compressions by applying firm, rapid compressions to the middle of the victim's chest, but not mouth-to-mouth manual The practice of breathing has been removed from the general population, but professional first aiders still need to perform these 30:2 steps.
cpr is the abbreviation for cardiopulmonary resuscitation. When the heart suddenly stops, if there is no immediate and timely rescue and resuscitation within 4-6 minutes, it will cause irreversible damage to the patient's brain and other important human organs and tissues. Therefore, cardiopulmonary resuscitation after cardiac arrest must be on-site. Immediately, cardiac arrest is unlike cardiac arrest at the end stage of any chronic disease. If effective resuscitation measures are taken in time, the patient may be saved and recover. In order to further rescue and save the life of the injured person who suffered cardiac arrest, precious time is gained.
Cardiac Arrest (CA) refers to the sudden cessation of the heart's pulsation in unexpected circumstances and time caused by various reasons, resulting in the sudden cessation of effective heart pump function and effective circulation, causing serious deficiency of tissue cells throughout the body. Blood, hypoxia and metabolic disorders can lead to immediate loss of life if not rescued in time. Cardiac arrest is different from cardiac arrest at the end stage of any chronic disease. If correct and effective resuscitation measures are taken in time, the patient may be saved and recover.
Once a cardiac arrest occurs, if immediate and timely rescue and resuscitation is not provided, irreversible damage to the patient's brain and other important human organs and tissues will occur within 4 to 6 minutes. Therefore, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (cpr) after cardiac arrest is ) must be carried out immediately at the scene to gain the most precious time for further rescue and saving the life of the cardiac arrest victim.
Since the anatomy, physiology, and development of children are different from those of adults, the manual cpr operations of children and adults are quite different. Children can be divided into three groups: newborns within 28 days of birth, infants between 0 and 1 years old, and children between 1 and 8 years old. Hands-on cpr for children over 8 years old is basically the same as for adults. The compression depth for infants generally requires a compression depth of 1 to 2 cm, which is about 1/3 of the thorax thickness. It can be flexibly controlled according to the patient's size and other conditions. The ideal effect is to touch the carotid artery pulse during compression.
Key words: cpr, cpr OPERATION,cardiopulmonary resuscitation