Half body CPR training manikin(Sim....

BIX/CPR100A
Advanced fully automatic electroni....
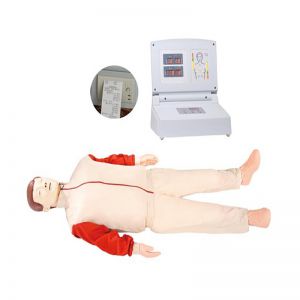
BIX/CPR480
Advanced computer half body CPR ma....

BIX/CPR260
Advanced infant head for trachea i....
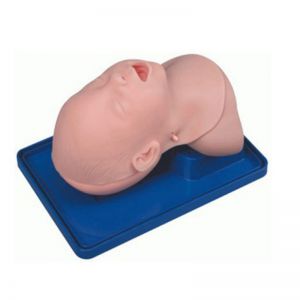
BIX-J3A
Neonate Head for trachea Intubatio....

BIX-J2A
Created on:2024-06-11 | bomn
Article tag: Laryngeal heart-lung model
The laryngeal cardiopulmonary model uses a variety of techniques and designs to ensure the accuracy and intuitiveness of the model when ...
The laryngeal cardiopulmonary model uses a variety of techniques and designs to ensure the accuracy and intuitiveness of the model when simulating the real structure. Here is a detailed explanation of how the laryngeal cardiopulmonary model mimics the real structure:
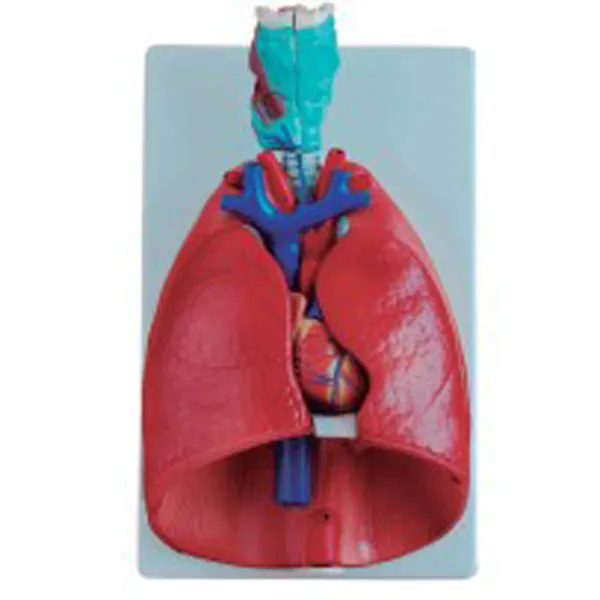
Size and proportion:
Laryngeal cardiopulmonary models are usually scaled down to the size and proportions of the real human larynx, heart and lungs. For example, some models may maintain the proportions of natural dimensions, such as 40cm high, 26cm wide, and 12cm deep, which helps users more intuitively understand the actual size of the organ.
Material selection:
The materials used in the models are mostly PVC or other durable materials, which are not only strong and durable enough, but also able to simulate the feel and appearance of real organs.
The surface of the model is often painted using paint and computer color matching techniques to more realistically represent the color and texture of the throat, heart and lungs.
Structure design:
The design of the model closely follows the structure of the real throat, heart and lungs. For example, the larynx model will show the larynx, vocal cords, trachea and other structures in detail; The heart model shows the connections of the atria, ventricles, valves and major blood vessels. The lung model simulates structures such as the lung lobes, bronchus and blood vessels.
To better show the internal structure, models are often designed to be removable. For example, two lobes of the lung can be removed to show its internal structure, and the heart can be dissected to show the atria, ventricles, and valves.
Detailed identification:
The model will have detailed labels or instructions indicating the names of various parts and structures. These identifiers help users more accurately identify and understand the various parts of the model.
Some advanced models also include numbers or code to interact with instructional software or apps to provide more detailed and dynamic information.
Functional design:
In addition to static displays, some laryngeal cardiopulmonary models have functional designs. For example, some laryngeal models can simulate the function of opening the loud door or closing the glottis to demonstrate the movement of laryngeal muscles; The heart model can simulate the beating of the heart and blood flow.
Interactivity:
Modern laryngeal cardiopulmonary models often have an interactive design, allowing users to interact with the model via touch screens, buttons, or other means. This interactivity not only adds interest to the model, but also helps users gain a deeper understanding of how the organ functions and works.
In summary, the laryngeal cardiopulmonary model simulates the structure and function of the real larynx, heart and lungs through a variety of ways, such as size and scale, material selection, structural design, detailed identification, functional design and interactivity. These designs and techniques ensure the accuracy and intuitiveness of the model, making it an indispensable tool in medical education, clinical training and research work.