Half body CPR training manikin(Sim....

BIX/CPR100A
Advanced fully automatic electroni....
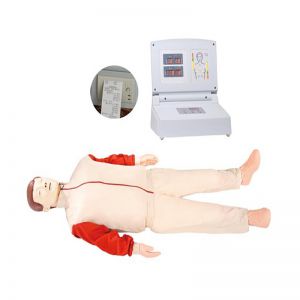
BIX/CPR480
Advanced computer half body CPR ma....

BIX/CPR260
Advanced infant head for trachea i....
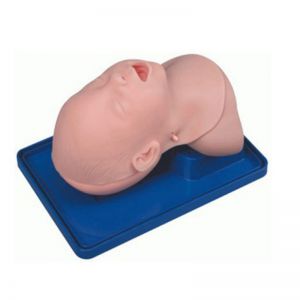
BIX-J3A
Neonate Head for trachea Intubatio....

BIX-J2A
Created on:2025-08-28 | bomn
Article tag: Bleeding control arm model BIX-G105-2
The bleeding control arm model is a professional device used in emergency rescue and clinical skills training. It is mainly used to simulate different bleeding conditions after upper limb trauma, helping trainees master hemostasis methods and rescue procedu...
The bleeding control arm model is a professional device used in emergency rescue and clinical skills training. It is mainly used to simulate different bleeding conditions after upper limb trauma, helping trainees master hemostasis methods and rescue procedures.
Its success criteria are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Firstly, trainees can quickly determine the type of bleeding (such as capillary, venous or arterial bleeding) based on the amount and location of the bleeding in the model, and select appropriate hemostasis measures.
Secondly, during the operation, one can skillfully apply methods such as direct compression, compression bandaging, elevating the affected limb, and tourniquet application, and effectively control bleeding within the limited time.
Secondly, after hemostasis, it is necessary to maintain the blood supply to the limbs to avoid tissue ischemic necrosis due to improper operation.
Finally, the entire operation should follow the aseptic principle, with standardized procedures and good coordination between language communication and operation.
If the bleeding is significantly reduced or completely stopped during the model exercise, the limb is firmly fixed and the vital signs of the affected limb are stable in the simulation, it can be determined as a success. Through the application of this model, learners can repeatedly train in a risk-free environment, improve their emergency response and clinical rescue capabilities, and lay a solid foundation for the safe treatment of actual bleeding patients.